|
|
|
Darcys Law & Effective Conductivities
|
|
|
|
|
Darcy's law and Effective Conductivity 2
When averaging over any spatial arrangement of discrete K values, the upscaling or averaging result depends on orientation of the arrangement relative to the direction of the hydraulic head gradient. and harmonic means
Use MAGNET to simulate the flow in heterogeneous porous media in the following 4 cases and compute and compare the specific discharge and effective conductivity values.
(Darcys Law & Effective Conductivities - 13)
|
|

|
|
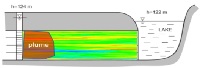
Darcy's law and Effective Conductivity 1
Darcy's law is an equation that states that flow through porous media is directly proportional to hydraulic head and inversely proportional to the length of flow. Use MAGNET to compute the effective conductivity, transmissivity of the aquifer below and the rate of flow between the two rivers.
(Darcys Law & Effective Conductivities - 13)
|
|

|
|
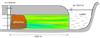
Effective Hydraulic Conductivity - Applied Lanfill Problem
A leachate mound in the landfill serves as a driving force for vertical and lateral loading of contaminants into a sand and gravel aquifer and the surrounding sloughs, respectively. Calculate the flux of leachate (seepage flux and contaminant flux) and travel times from the landfill to the sloughs and underlying aquifer, and use MAGNET to simulate leachate offsite migration in the deep aquifer.
(Darcys Law & Effective Conductivities - 13)
|
|
|
|
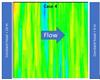
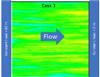
Small scale Heterogeneity vs Large Scale Anisotropy
It is well know that hydraulic conductivity field in real-world aquifers are strongly heterogeneous, exhibiting multiple scales of variations. Use MAGNET to demonstrate small scale heterogeneity has large sale implications: small scale heterogeneites translate into large scale anisotropy.
(Darcys Law & Effective Conductivities - 13)
|
|
|
|
Contaminant Transport in Stochastically Stratified Media
This problem considers the movement of a benzene plume in a stochastically stratified confined aquifer toward a lake used for recreation and drinking water supply. Using MAGNET, asses the risk, or probability of the contaminant concentration exceeding the MCL at the aquifer-lake interface.
(Darcys Law & Effective Conductivities - 13)
|
|
|
|
Contaminant Transport in an Aquifer - Homogeneous vs. Stratified
This problem considers the movement of a benzene plume in a confined aquifer toward a lake used for recreation and drinking water supply. Using MAGNET, asses the risk, or probability of the contaminant concentration exceeding the MCL at the aquifer-lake interface. Analyze and compare the following situations i) a homogeneous aquifer; ii) a stratified aquifer; and iii) a stochastically stratified aquifer.
(Darcys Law & Effective Conductivities - 13)
|
|
|
|